Introduction to Solar Inverters
In the world of renewable energy, solar power has become an increasingly popular choice for homeowners, businesses, and industries. One of the most vital components in a solar energy system is the solar inverter. A solar inverter plays a critical role in converting solar energy into usable electricity, making it essential for any solar power setup. This guide will explore what solar inverters are, how they work, the types available, and their benefits.
What is a Solar Inverter?
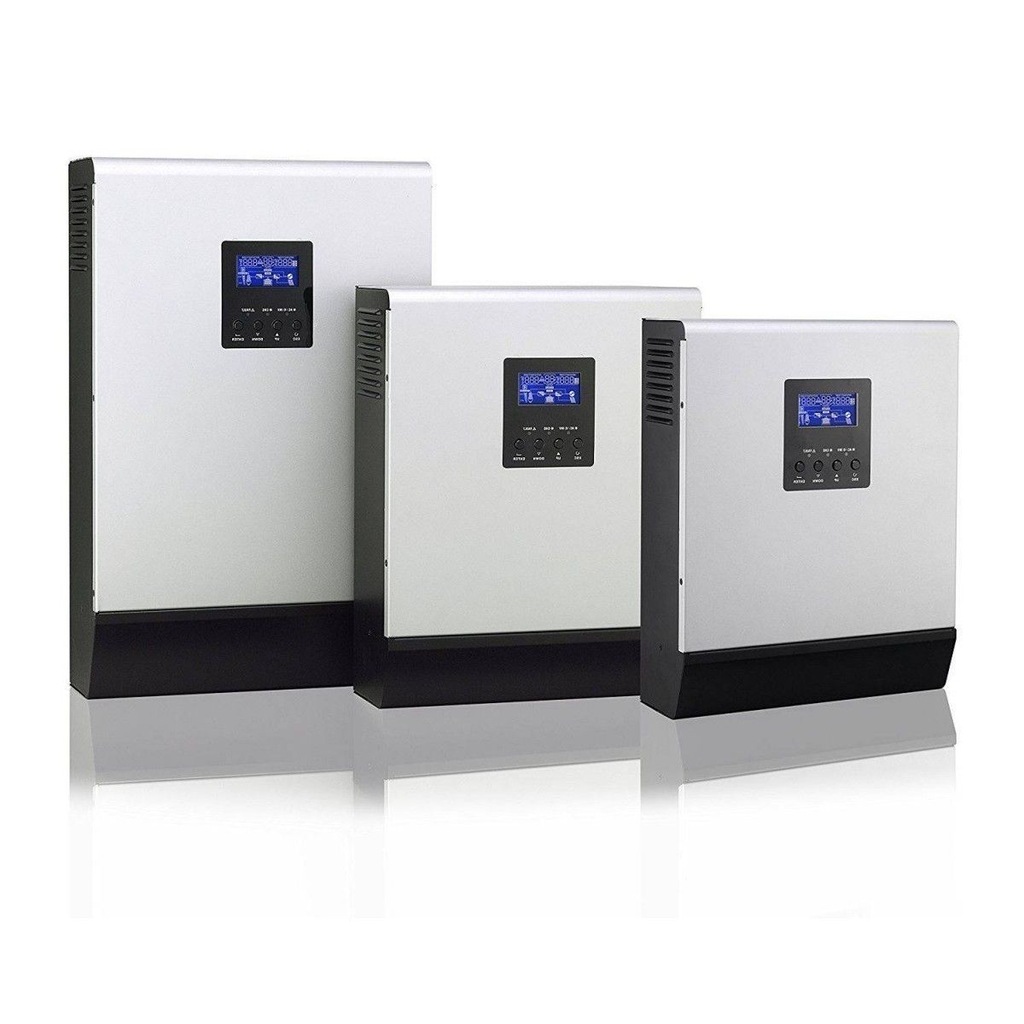
A solar inverter is an electrical device that converts the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC), the standard form of electricity used by most appliances and the electrical grid. Without a solar inverter, the DC electricity produced by the solar panels cannot be directly used in homes or businesses.
How Do Solar Inverters Work?
- DC Electricity Generation: Solar panels absorb sunlight, generating DC electricity.
- Inversion Process: The solar inverter converts the DC electricity into AC electricity.
- Power Supply: The AC electricity is then distributed to power appliances or sent back to the grid, depending on the setup.
By performing this conversion, solar inverters make solar energy functional and useful for everyday applications.
Types of Solar Inverters
There are several types of solar inverters available, each designed for specific needs and setups:
1. String Inverters
- Overview: String inverters are commonly used in residential and small commercial installations.
- Functionality: They connect a series (or “string”) of solar panels to a single inverter, making them cost-effective and straightforward to install.
- Best for Installations with consistent sunlight and minimal shading.
2. Microinverters
- Overview: Microinverters are installed on each solar panel, allowing individual panel optimization.
- Functionality: Unlike string inverters, microinverters work independently, so each panel produces the maximum power possible, even if others are shaded.
- Best for: Areas with shading issues or irregular roof angles.
3. Hybrid Inverters
- Overview: Hybrid inverters can manage both solar power and battery storage, making them ideal for off-grid and backup systems.
- Functionality: They allow users to store excess energy in batteries for later use, providing energy security and flexibility.
- Best for Users looking to combine solar and battery systems for enhanced energy independence.
4. Central Inverters
- Overview: Central inverters are larger and designed for industrial and large commercial applications.
- Functionality: They connect multiple solar strings into a single inverter, providing efficient and centralized power conversion.
- Best for: Large-scale installations with significant energy demands.
5. Battery Inverters
- Overview: Battery inverters are specifically used in setups with battery storage systems.
- Functionality: They convert stored DC power from batteries into AC electricity, helping to maintain a continuous power supply during grid outages.
- Best for: Off-grid applications or areas with unreliable grid power. Read More: Commercial Electrician
Key Benefits of Solar Inverters
- Energy Efficiency: By converting DC to AC, solar inverters make solar power usable, maximizing energy efficiency.
- Monitoring and Management: Many modern inverters offer monitoring features, allowing users to track energy production and system performance.
- Grid Connection: Inverters enable a seamless connection between solar systems and the grid, facilitating net metering and energy sales.
- Flexibility and Scalability: With various types of inverters available, users can choose the best option for their specific needs, from small residential setups to large commercial installations.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Solar Inverter
1. System Size and Capacity
- Choose an inverter that matches the size of your solar array and meets your energy needs.
2. Budget and Cost
- Inverters vary in cost; consider both the upfront investment and potential long-term savings.
3. Shading and Roof Orientation
- For areas with shading issues, microinverters may be more suitable, while string inverters work well in consistent sunlight.
4. Monitoring Capabilities
- Some inverters come with built-in monitoring systems, allowing you to track and optimize your energy production.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Solar Inverters
Routine Maintenance
- Regularly inspect your inverter for dust, debris, and proper ventilation.
- Check for software updates to ensure your inverter operates at peak efficiency.
Common Issues
- Overheating: Ensure proper ventilation to prevent overheating, which can reduce inverter efficiency.
- Error Codes: Many inverters display error codes when issues arise; consult the manual or technician for solutions.
Conclusion
Solar inverters are the heart of any solar power system, enabling the conversion of sunlight into usable electricity. With a range of types suited to various needs, selecting the right inverter can enhance energy efficiency, provide monitoring options, and even integrate battery storage. By understanding the functions, benefits, and types of solar inverters, users can make informed decisions, maximizing the effectiveness of their solar energy systems.